Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 MOE Key Laboratory of Laser Life Science and Institute of Laser Life Science, College of Biophotonics, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510631, China
2 Guangzhou Key Laboratory for Special Fiber Photonic Devices, School of Information and Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510006, China
3 School of Physical Education and Sports Science, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510006, China
4 Department of Data and Computer Science, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510006, China
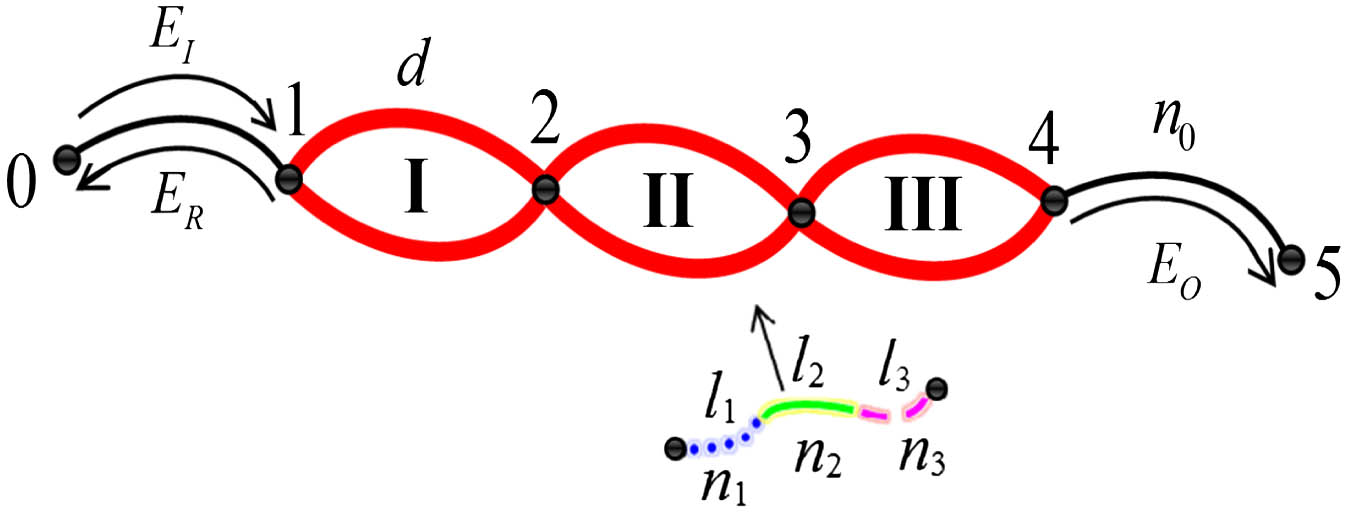
In this paper, we design a one-dimensional (1D) parity-time-symmetric periodic ring optical waveguide network (PTSPROWN) and investigate its extraordinary optical characteristics. It is found that quite different from traditional vacuum/dielectric optical waveguide networks, 1D PTSPROWN cannot produce a photonic ordinary propagation mode, but can generate simultaneously two kinds of photonic nonpropagation modes: attenuation propagation mode and gain propagation mode. It creates neither passband nor stopband and possesses no photonic band structure. This makes 1D PTSPROWN possess richer spontaneous PT-symmetric breaking points and causes interesting extremum spontaneous PT-symmetric breaking points to appear, where electromagnetic waves can create ultrastrong extraordinary transmission, reflection, and localization, and the maximum can arrive at 6.6556×1012 and is more than 7 orders of magnitude larger than the results reported previously. 1D PTSPROWN may possess potential in designing high-efficiency optical energy saver devices, optical amplifiers, optical switches with ultrahigh monochromaticity, and so on.
Waveguides Optical materials Metamaterials Photonics Research
2018, 6(6): 06000579

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Nanophotonic Functional Materials and Devices, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510631, China
2 CAS Key Laboratory of Geospace Environment, University of Science & Technology of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230026, China
We present an investigation on the propagation properties of the chirped Airy vortex (CAiV) beams through slabs of left-handed materials (LHMs) and right-handed materials (RHMs). We discuss the influence of chirped parameter C on the propagation of the CAiV beams through LHM and RHM slabs. Our simulation results show that a maximum accelerated velocity appears during the propagation process. The intensity concentration of the CAiV beams increases with the absolute value of the chirped parameter. The peak intensity of the CAiV beams changes abruptly, and the chirped parameter plays an active role on the difference of the maximum and the minimum. In the energy flow, we find that the effects of the chirped parameter on the strength of the vortex are different at different propagation distances.
050.4865 Optical vortices 140.3295 Laser beam characterization 140.7010 Laser trapping 350.5500 Propagation Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(6): 060501
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Nanophotonic Functional Materials and Devices, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510631, China
2 CAS Key Laboratory of Geospace Environment, University of Science & Technology of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei 230026, China
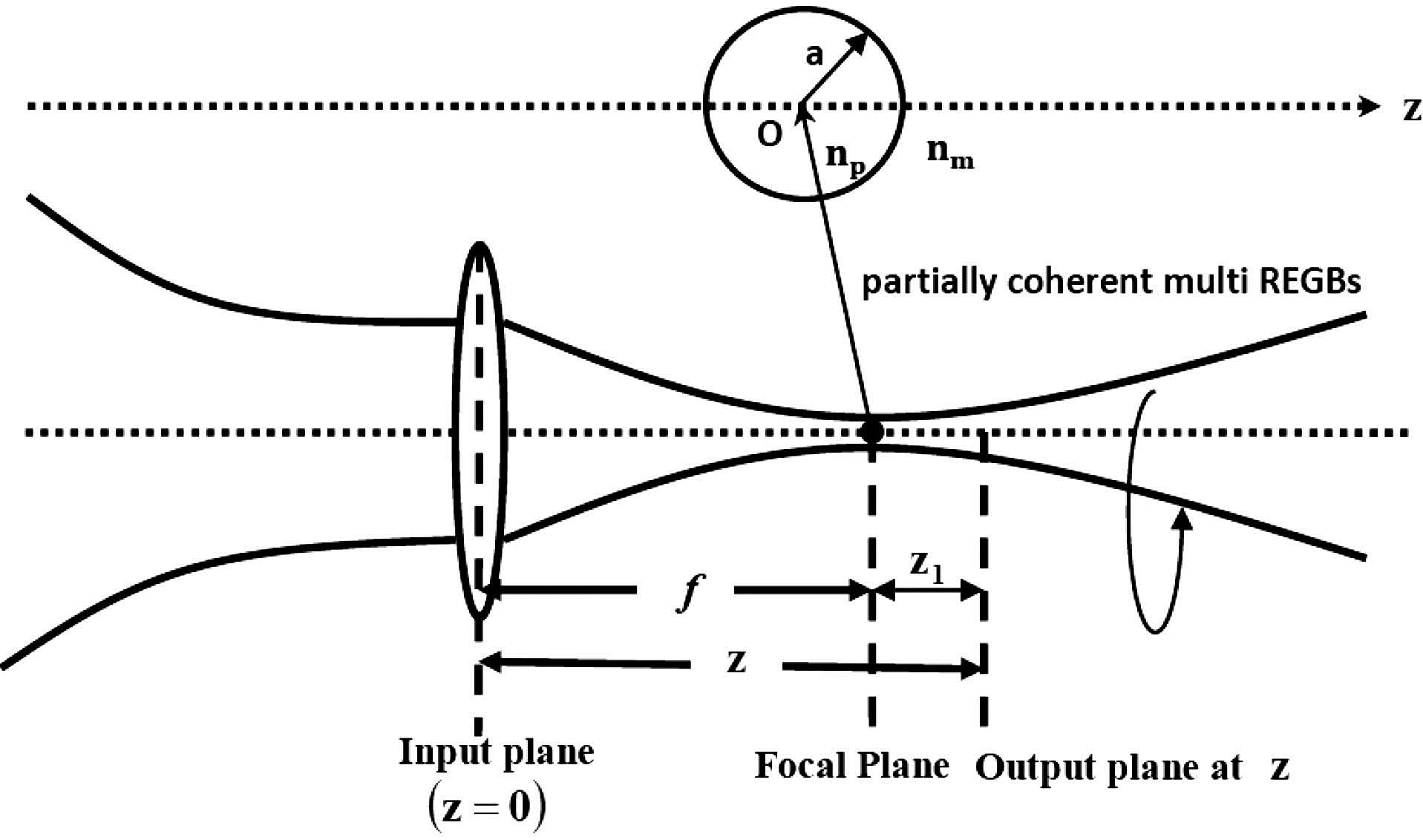
By investigating the cross-spectral density of partially coherent multi-rotating elliptical Gaussian beams (REGBs) that propagate through a focusing optical system, we obtain the radiation force on a Rayleigh particle. The radiation force distribution is studied under different beam indexes, coherence widths, and elliptical ratios of the partially coherent multi REGBs. The transverse and the longitudinal trapping ranges can increase at the focal plane by increasing the beam index or decreasing the coherence width. The range of the trapped particle radii increases as the elliptical ratio increases. Furthermore, we analyze the trapping stability.
140.3295 Laser beam characterization 140.7010 Laser trapping 350.5500 Propagation Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(1): 011405
Author Affiliations
Abstract
We theoretically and experimentally study self-accelerating and self-breathing Bessel-like beams that follow arbitrary trajectories, including hyperbolic, hyperbolic secant, and three-dimensional (3D) spiraling trajectories. The beams have an overall Bessel-like profile in transverse dimensions; however, the intensity of their central main lobe breathes while traveling along a curved trajectory. Such beams can be readily generated experimentally through appropriate phase modulation of the optical wavefront. The beams contribute to the design of new families of self-accelerating beams.
070.7345 Wave propagation 070.6120 Spatial light modulators 070.2580 Paraxial wave optics 090.1760 Computer holography Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(11): 110701
1 华南师范大学激光运动医学实验室, 广东 广州 510006
2 华南师范大学广东省微纳光子功能材料与器件重点实验室, 广东 广州 510006
研究了经无像差透镜聚焦的高斯光束在焦平面附近的群速度与相速度,阐明了由于衍射导致相位变化从而产生的超光速传播现象。给出了透镜几何焦点与光束束腰间距的微小变化对相速度与群速度的影响。
物理光学 超光速传播 会聚高斯光束 相位异常 激光与光电子学进展
2013, 50(6): 062602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Physics, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
In accordance with nonperturbative quantum scattering theory, we investigate photoelectron angular distributions (PADs) from above-threshold detachment (ATD) of negative ions irradiated by circularly polarized few-cycle laser fields. Electrons ejected on the polarization plane demonstrate distinct anisotropies in angular distributions which distinctly vary with the carrier-envelope (CE) phase. The anisotropy is caused by interference between transition channels; it also depends strongly on laser frequency, pulse duration, and kinetic energy of photoelectrons. Optimal emission of photoelectrons, which varies with CE phase, makes it possible to control photoelectron motion.
光电子角分布 双光子电离 激光波长 020.4180 Multiphoton processes 020.2649 Strong field laser physics Chinese Optics Letters
2011, 9(1): 010202
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Physics, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
Photoelectron angular distributions (PADs) from two-photon ionization of atoms in linearly polarized strong laser fields are obtained in accordance with the nonperturbative quantum scattering theory. We also study the influence of laser wavelength on PADs. For two-photon ionization very close to the ionization threshold, most of the ionized electrons are vertically ejected to the laser polarization. PADs from two-photon ionization of atoms are determined by the second order generalized phased Bessel function at which the ponderomotive parameter plays a key role. In terms of dependence of PADs on laser wavelength, corresponding variations for the ponderomotive parameter are demonstrated.
光电子角分布 阈上离解 周期量级激光场 020.4180 Multiphoton processes 020.2649 Strong field laser physics Chinese Optics Letters
2011, 9(1): 010203





